1. Treatment of convulsive status epilepticus. Recommendations of the epilepsy foundation of America’s working group on status epilepticus. JAMA. 1993;270:854–9.

2. Lowenstein DH, Bleck T, Macdonald RL. It’s time to revise the definition of status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1999;40:120–2.


3. Brophy GM, Bell R, Classen J, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation and management of status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2012;17:3–23.


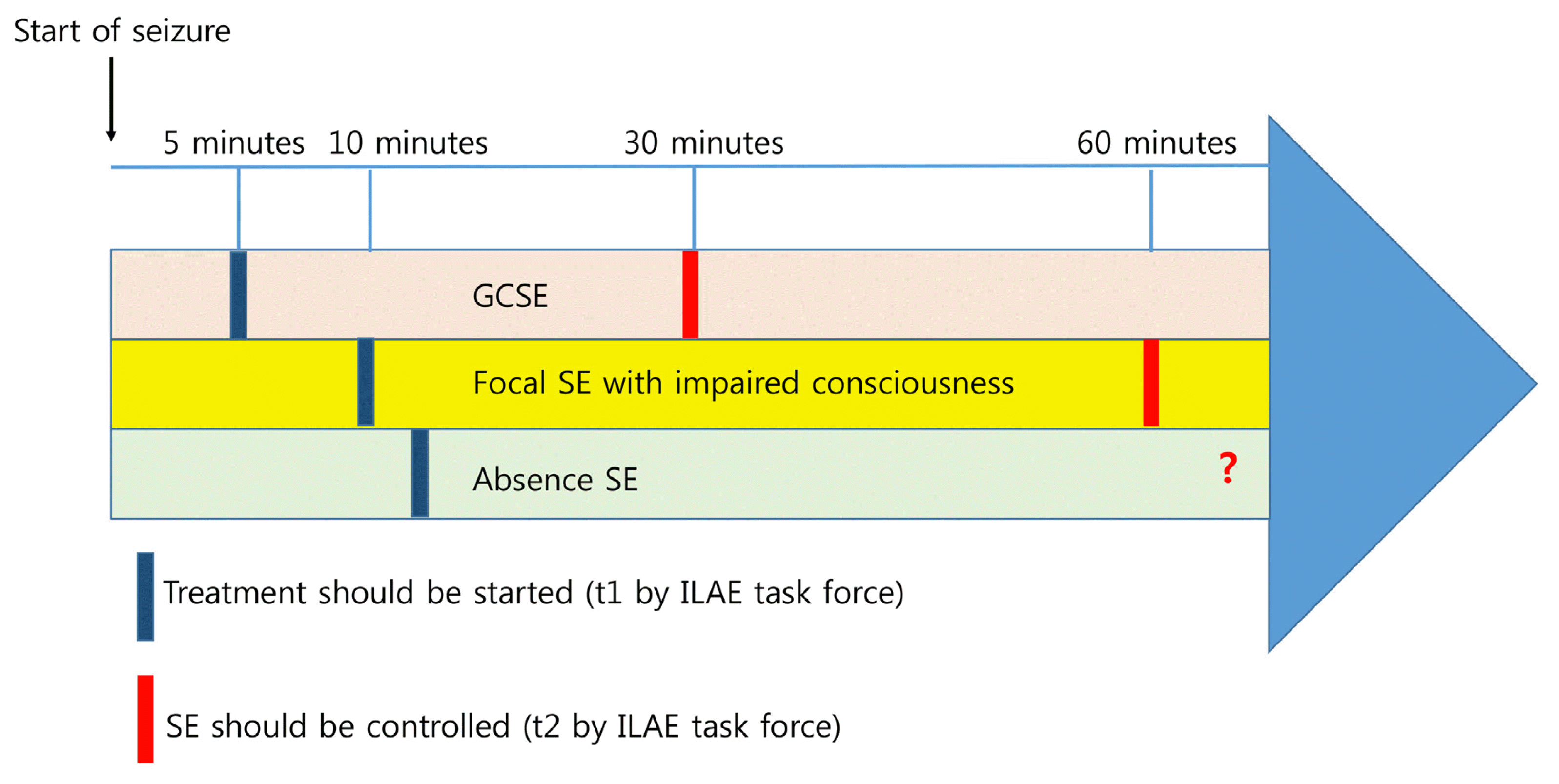
4. Trinka E, Cock H, Hesdorffer D, et al. A definition and classification of status epilepticus--report of the ILAE task force on classification of status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2015;56:1515–23.


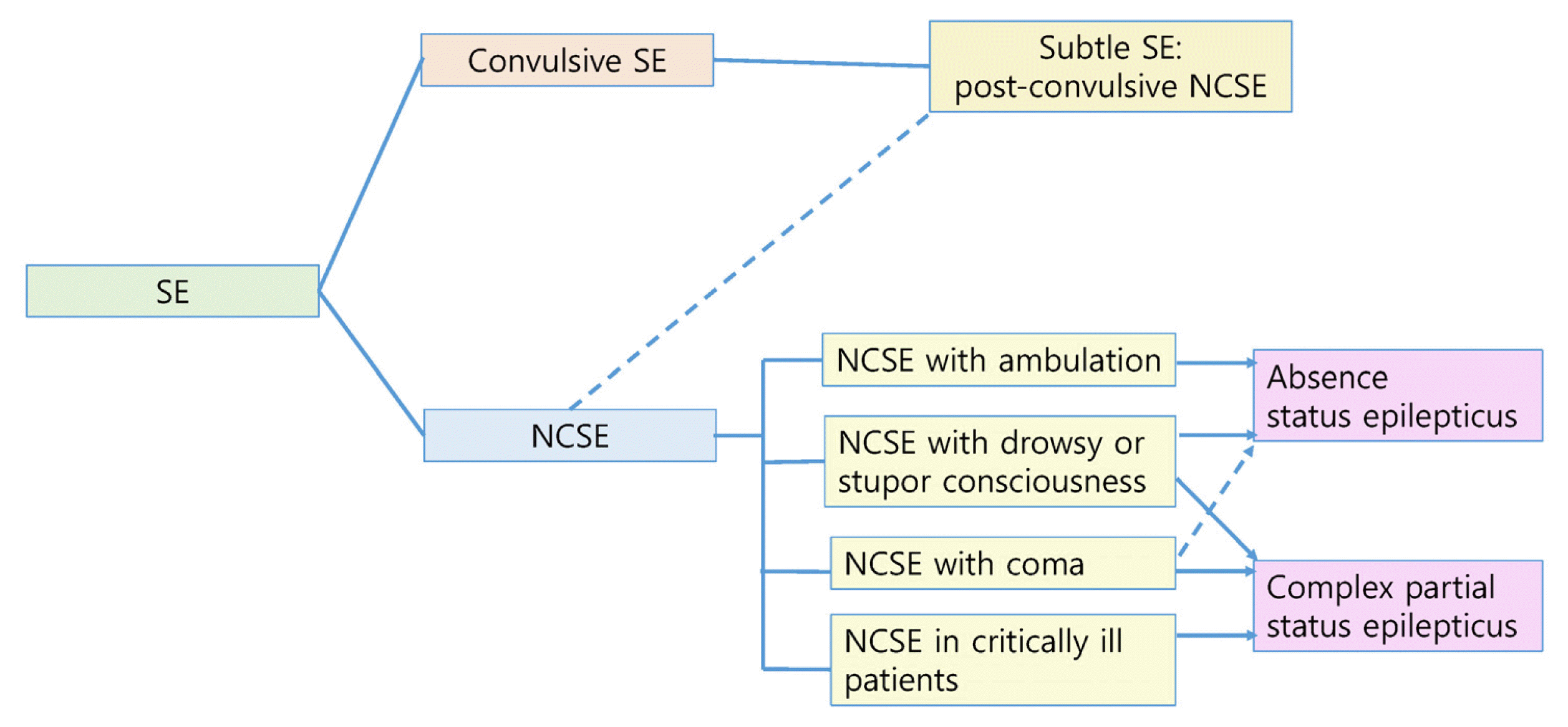
5. Walker M, Cross H, Smith S, et al. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus: Epilepsy Research Foundation workshop reports. Epileptic Disord. 2005;7:253–96.
6. Husain AM. Treatment of recurrent electrographic nonconvulsive seizures (TRENdS) study. Epilepsia. 2013;54:Suppl 6. 84–8.

7. Kaplan PW. Clinical presentations of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Drislane FW, Kaplan PW, editors. Status epilepticus: a clinical perspective. 2nd ed. New York: Springer Nature; 2018. p. 241–58.
8. Drislane FW. Presentation, evaluation, and treatment of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2000;1:301–14.

9. Thomas P, Zifkin B, Andermann F. Absence status. Wasterlain CG, Treiman DM, editors. Status epilepticus: mechanisms and management. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2006. p. 91–108.
10. Thomas P, Andermann F. Absence status in elderly patients is most often situation-related. Malfosse A, Genton P, Hirsch E, Marescaux C, Broglin D, Bernasconi R, editors. Idiopathic generalized epilepsies: clinical, experimental and genetic aspects. UK ed. London: John Libbey; 1994. p. 95–109.
11. Thomas P, Beaumanoir A, Genton P, Dolisi C, Chatel M. ‘De novo’ absence status of late onset: report of 11 cases. Neurology. 1992;42:104–10.


12. Thomas P, Zifkin B, Migneco O, Lebrun C, Darcourt J, Andermann F. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus of frontal origin. Neurology. 1999;52:1174–83.


13. Kaplan PW. Behavioral manifestations of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2002;3:122–39.


14. Bleck TP. Refractory status epilepticus. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005;11:117–20.


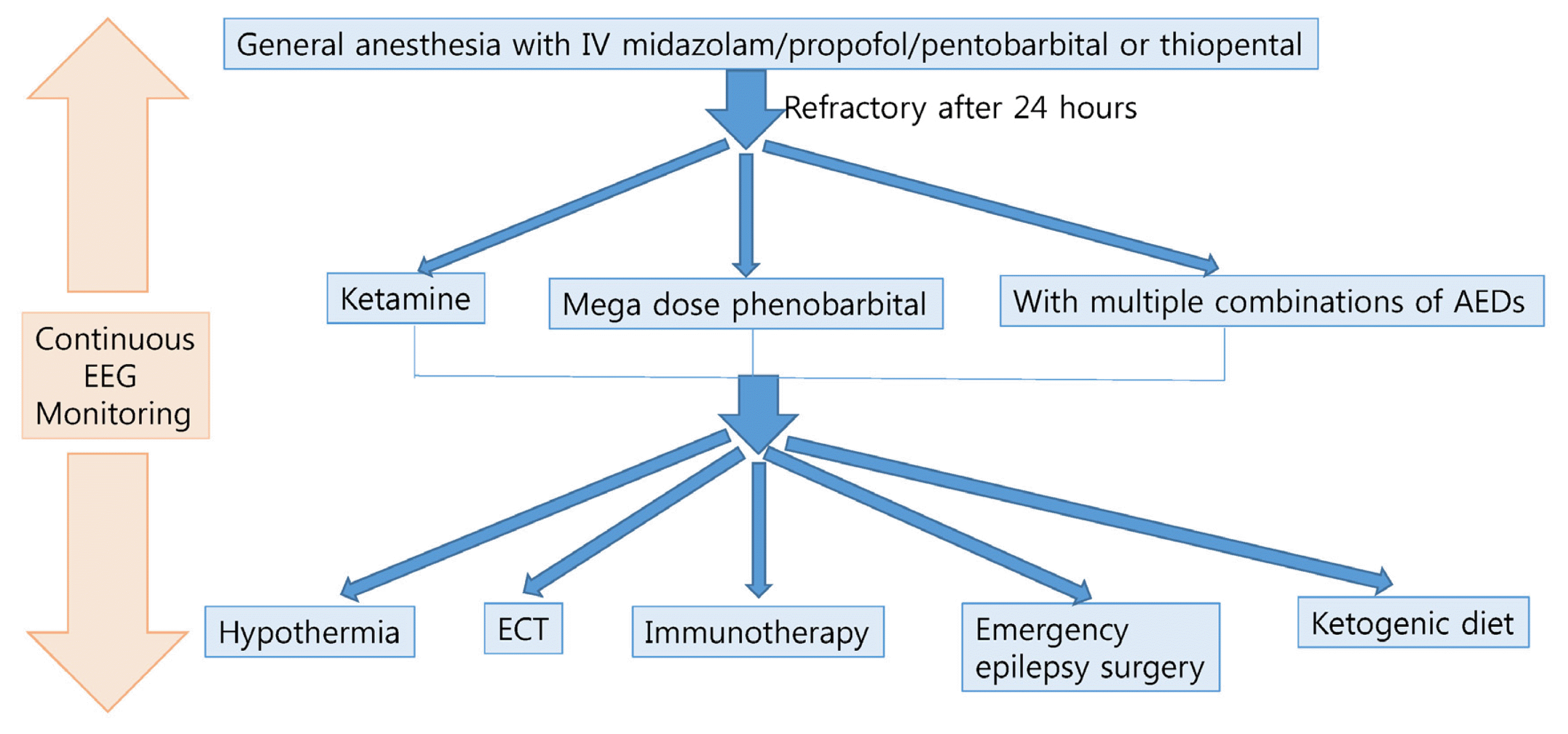
15. Shorvon S, Ferlisi M. The treatment of super-refractory status epilepticus: a critical review of available therapies and a clinical treatment protocol. Brain. 2011;134:Pt 10. 2802–18.


17. Meierkord H, Boon P, Engelsen B, et al. EFNS guideline on the management of status epilepticus in adults. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17:348–55.


18. Shorvon S. What is nonconvulsive status epilepticus, and what are its subtypes? Epilepsia. 2007;48:Suppl 8. 35–8.

19. Herman ST. The electroencephalogram of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Kaplan PW, Drislane FW, editors. Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus. New York: Demos Medical Publishing; 2009. p. 41–62.
20. Young GB, Jordan KG, Doig GS. An assessment of nonconvulsive seizures in the intensive care unit using continuous EEG monitoring: an investigation of variables associated with mortality. Neurology. 1996;47:83–9.


21. Mikati MA, Lee WL, DeLong GR. Protracted epileptiform encephalopathy: an unusual form of partial complex status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1985;26:563–71.


22. Markand ON, Wheeler GL, Pollack SL. Complex partial status epilepticus (psychomotor status). Neurology. 1978;28:189–96.


23. Ballenger CE, King DW, Gallagher BB. Partial complex status epilepticus. Neurology. 1983;33:1545–52.


24. Thomas P, Zifkin B, Andermann F. Simple and complex partial status epilepticus. Wasterlain CG, Treiman DM, editors. Status Epilepticus: Mechanisms and Management. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2006. p. 69–90.
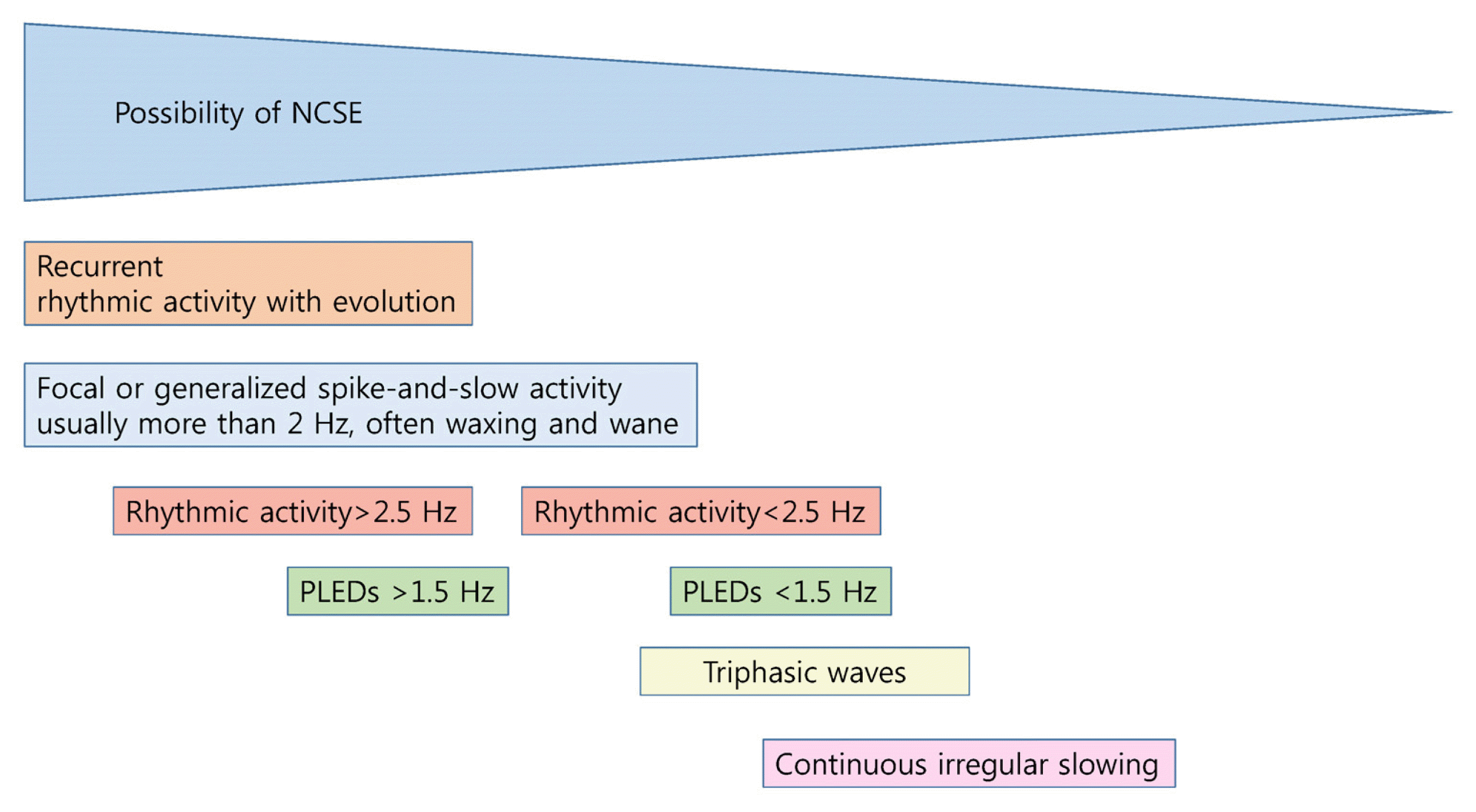
25. Chong DJ, Hirsch LJ. Which EEG patterns warrant treatment in the critically ill? Reviewing the evidence for treatment of periodic epileptiform discharges and related patterns. J Clin Neurophsiol. 2005;22:79–91.

26. Kaplan PW. The EEG of status epilepticus. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;23:221–9.


27. Brigo F, Storti M. Triphasic waves. Am J Electroneurodiagnostic Technol. 2011;51:16–25.


28. Snodgrass SM, Tsuburaya K, Ajmone-Marsan C. Clinical significance of periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges: relationship with status epilepticus. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1989;6:159–72.


29. Brenner RP. Is it status? Epilepsia. 2002;43:Suppl 3. 103–13.

30. Navarro V, Fischer C, Convers P. Differential diagnosis of status epilepticus. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2009;165:321–7.


31. Brophy GM, Bell R, Claassen J, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation and management of status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2012;17:3–23.


33. Treiman DM. The role of benzodiazepines in the management of status epilepticus. Neurology. 1990;40:5 Suppl 2. 32–42.

34. Leppik IE, Derivan AT, Homan RW, Walker J, Ramsay RE, Patrick B. Double-blind study of lorazepam and diazepam in status epilepticus. JAMA. 1983;249:1452–4.

35. Silbergleit R, Lowenstein D, Durkalski V, Conwit R. Neurological Emergency Treatment Trials (NETT) Investigators. RAMPART (rapid anticonvulsant medication prior to arrival trial): a double-blind randomized clinical trial of the efficacy of intramuscular midazolam versus intravenous lorazepam in the prehospital treatment of status epilepticus by paramedics. Epilepsia. 2011;52:Suppl 8. 45–7.

36. Yasiry Z, Shorvon SD. The relative effectiveness of five antiepileptic drugs in treatment of benzodiazepine-resistant convulsive status epilepticus: a meta-analysis of published studies. Seizure. 2014;23:167–74.


37. Chamberlain JM, Kapur J, Shinnar S, et al. Efficacy of levetiracetam, fosphenytoin, and valproate for established status epilepticus by age group (ESETT): a double-blind, responsive-adaptive, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1217–24.


38. Nakamura K, Inokuchi R, Daidoji H, et al. Efficacy of levetiracetam versus fosphenytoin for the recurrence of seizures after status epilepticus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e7206

39. Brigo F, Nardone R, Tezzon F, Trinka E. Nonintravenous midazolam versus intravenous or rectal diazepam for the treatment of early status epilepticus: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2015;49:325–36.


40. Power KN, Gramstad A, Gilhus NE, Engelsen BA. Adult nonconvulsive status epilepticus in a clinical setting: semiology, aetiology, treatment and outcome. Seizure. 2015;24:102–6.

41. Olney JW, Collins RC, Sloviter RS. Excitotoxic mechanisms of epileptic brain damage. Adv Neurol. 1986;44:857–77.
42. Meldrum BS. Excitotoxicity and selective neuronal loss in epilepsy. Brain Pathol. 1993;3:405–12.


43. Strzelczyk A, Zöllner JP, Willems LM, et al. Lacosamide in status epilepticus: systematic review of current evidence. Epilepsia. 2017;58:933–50.


45. Rosati A, De Masi S, Guerrini R. Ketamine for refractory status epilepticus: a systematic review. CNS Drugs. 2018;32:997–1009.


46. Byun JI, Chu K, Sunwoo JS, et al. Mega-dose phenobarbital therapy for super-refractory status epilepticus. Epileptic Disord. 2015;17:444–52.


47. Kim DW, Gu N, Jang IJ, et al. Efficacy, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine oral loading in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2012;53:e9–12.


48. Fechner A, Hubert K, Jahnke K, et al. Treatment of refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus with topiramate: a cohort study of 106 patients and a review of the literature. Epilepsia. 2019;60:2448–58.


49. Ho CJ, Lin CH, Lu YT, et al. Perampanel treatment for refractory status epilepticus in a neurological intensive care unit. Neurocrit Care. 2019;31:24–9.


50. Walker MC. Pathophysiology of status epilepticus. Neurosci Lett. 2018;667:84–91.


51. Arya R, Rotenberg A. Dietary, immunological, surgical, and other emerging treatments for pediatric refractory status epilepticus. Seizure. 2019;68:89–96.


53. Sculier C, Gaspard N. New onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE). Seizure. 2019;68:72–8.


54. Gaspard N, Hirsch LJ, Sculier C, et al. New-onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE) and febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES): state of the art and perspectives. Epilepsia. 2018;59:745–52.


55. Hirsch LJ, Gaspard N, van Baalen A, et al. Proposed consensus definitions for new-onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE), febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES), and related conditions. Epilepsia. 2018;59:739–44.

56. Jun JS, Lee ST, Kim R, Chu K, Lee SK. Tocilizumab treatment for new onset refractory status epilepticus. Ann Neurol. 2018;84:940–5.